SharePoint Admin Center: How to Manage SharePoint Sites
What is the SharePoint Admin Center? It is the web interface that provides SharePoint Online administrators with all the tools needed to manage sites, content, and data security in a centralized way.
In this article, we will explore the features of the SharePoint Admin Center along with our tips for using them effectively.

What you will find in this article
SharePoint Admin Center: What is it and what is it for?
SharePoint Online is the most famous and widely used Microsoft 365 platform for creating modern sites, supporting team collaboration (in the case of collaboration sites) and simplifying internal communication. The latter is the case for communication sites, such as the company intranet, with features for content management, from documents to news.
To function optimally, ensuring the best user experience and data privacy, SharePoint provides a dedicated web interface where only Admin users can access the necessary configurations to manage corporate sites.
This is the SharePoint Admin Center, the hub for managing SharePoint Online in Microsoft 365.
This centralized interface provides the tools to:
- Create new sites in your SharePoint Online instance
- Manage access to content and information stored in SharePoint
- Monitor the operation of active SharePoint sites, including space usage
- Implement policies to support collaboration, with a focus on security
And much more, which we will explore in detail in this article.
Guide to the Admin Center of SharePoint Online
SharePoint Admin Center: How to access?
The SharePoint Admin Center is accessible only to administrators with an Office 365 subscription, which of course includes SharePoint Online.
Global administrators within the Microsoft 365 tenant hold the highest level of permissions, having access to all the features offered in the SharePoint Admin Center.
However, they can grant access permissions to the admin center to other users by assigning them the Admin role for:
- Manage SharePoint site collections
- Set storage quotas
- Oversee other admins and site owners
To assign the Admin role in SharePoint, global administrators must:
- Access the Microsoft 365 admin center
- Select the "Roles" option
- Select the "Role Assignments" option on the left
- Double-click the "SharePoint Administrator" role
- Select the "Add users" command
- Add the users to whom the role will be assigned
Users entered in the list are then enabled to manage SharePoint Online and its sites, using the available configurations in the SharePoint Admin Center. How to reach it?
At this point, Admin users just need to:
- Go to the address admin.microsoft.com
- Log in with your Office 365 credentials
- Select the admin center for SharePoint, scrolling in the left panel
By clicking on the "SharePoint" option, Admin users are redirected to the SharePoint Admin Center, where they will find all the tools to manage the corporate SharePoint environment effectively.
SharePoint Admin Center: What features does it offer?
Here’s what the Admin Center provides to improve the user experience and ensure maximum security of corporate data within SharePoint Online sites.
Below are the most important configuration areas (located in the left navigation bar of the Admin Center’s main interface). Each of these areas contains specific settings to define policies, adjust sharing options, oversee the structure of site collections, and much more.
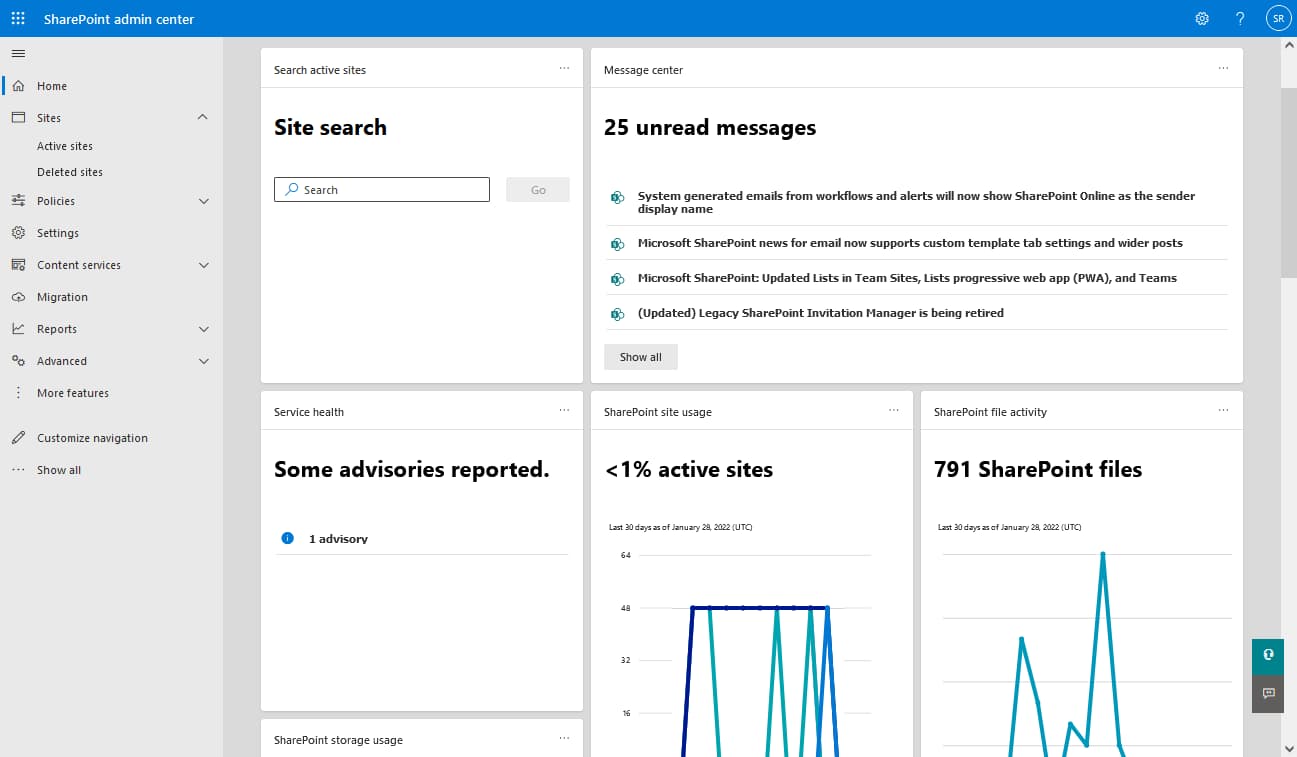
SharePoint Admin Center home page
On the SharePoint Admin Center home page, the first important information about the status of your SharePoint Online instance is provided. The dashboards are displayed, providing real-time updated data on:
- Corporate site usage in the last 30 days
- Service status
- System updates
The system updates represent messages from Microsoft, which inform administrators about improvements, new features, and any changes made to SharePoint that could affect the user experience.
There is also a search bar that can be used to retrieve active SharePoint sites and monitor their usage. For example, the occupied storage space.
SharePoint Admin Center home page
The occupied quota of the SharePoint sites is located at the top right, where a simple graphic shows the occupied space compared to the remaining available space for the company.
This overview of available storage is essential for proper SharePoint management.
It should be noted that the storage space for SharePoint Online provides 1TB per company, plus 10GB for each licensed user that includes SharePoint. For example, a company with 100 users with a Microsoft 365 license that includes SharePoint Online will have 1TB + (10GB * 100) = 2TB of space.
Once this quota is exceeded, access is blocked to almost all document storage and sharing features within SharePoint Online.
If more than 12 months pass without the company purchasing additional storage space, Microsoft may disable the account and permanently delete all the content.
In addition to an overview of the current memory status, SharePoint’s Admin Center does not offer useful tools to prevent exceeding the available quota. It only allows deleting sites within the instance.
To manage their storage space, companies have three alternatives available:
- Purchase new storage space for SharePoint, before exceeding the quota. This is likely the least cost-effective option, as the price is €0.2/GB/month.
- Purchase Microsoft 365 Archive, the solution that Microsoft has designed specifically to offer additional storage space for SharePoint sites. A more cost-effective option than directly purchasing new memory, with a price of €0.05/GB/month.
- Consult experts such as intranet.ai, to learn how to manage SharePoint, Teams, and OneDrive storage space autonomously, saving on the purchase of new memory and external products like Microsoft 365 Archive.
Our experts can indeed provide companies with the tools and knowledge necessary to reduce the space occupied by SharePoint and OneDrive.
With a few days of consulting, we can train users on how to maintain clean archives in the corporate cloud, focusing on their management rather than their location (this is not a simple migration from one archive to another).
It then becomes possible to:
- Improve the management of storage space in Microsoft 365, autonomously.
- Maintain collaboration features, which are lost with Microsoft 365 Archive.
Free up space with intranet.ai
Our consulting service is the best solution for managing your space in the Microsoft 365 cloud,
saving on the purchase of new storage and products such as Microsoft 365 Archive.
We will help your company to:
- Free up space in SharePoint, Teams, and OneDrive while maintaining collaboration capabilities.
- Manage archives in the enterprise Microsoft 365 environment independently.
- Implement custom rules and automations for cleaning archives.
Active sites, to manage active SharePoint sites
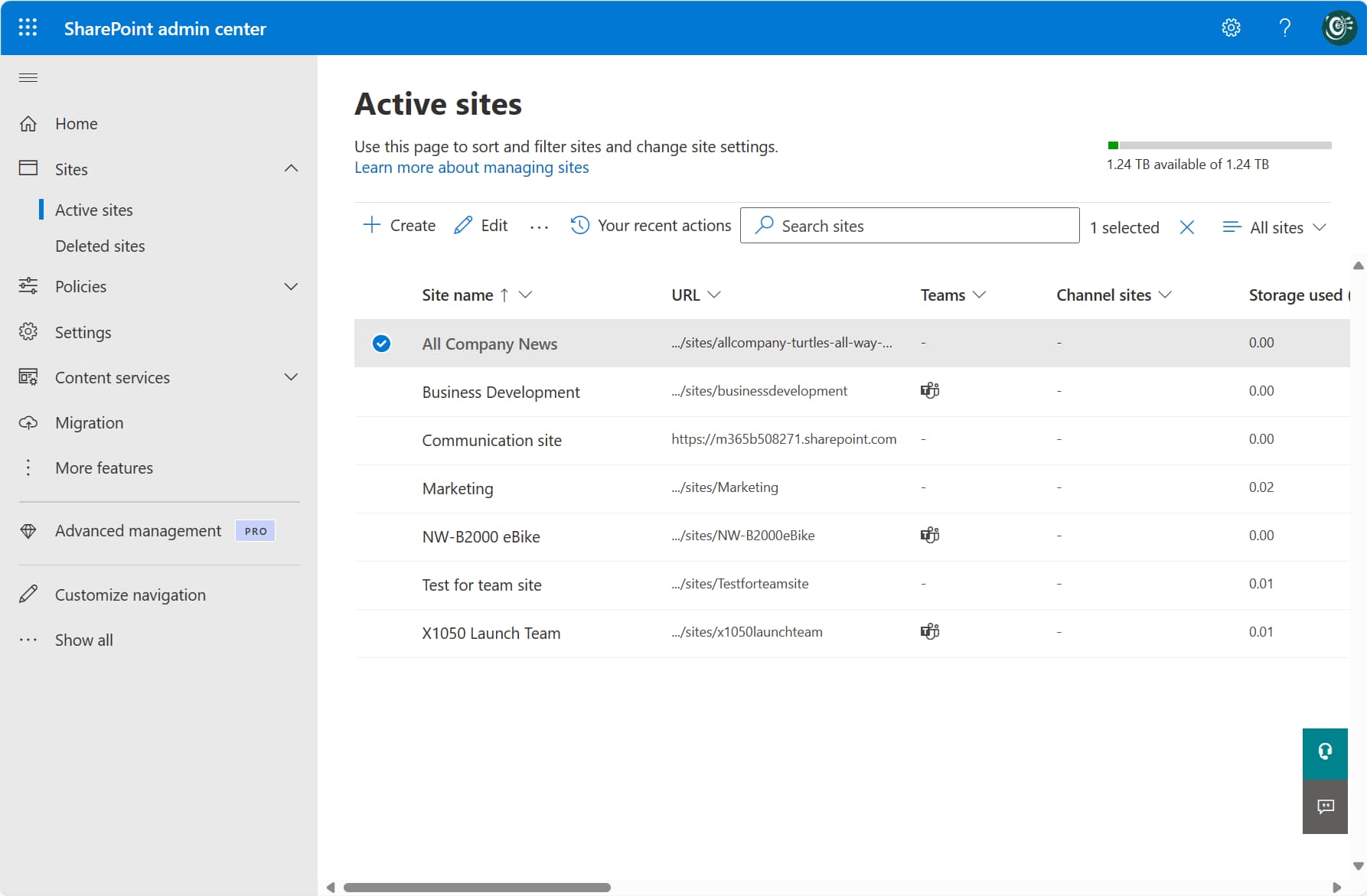
As an alternative to the search bar on the home page, administrators can view, from the "Active sites" option (located on the left, under the "Sites" section), the list of active SharePoint sites in the organization’s tenant.
This page is not only useful for viewing active sites. Each site in the list is accompanied by a set of useful information to understand its history and key configurations. Among these details, for each site, we find:
- Any Microsoft Teams group or channel connected (to understand whether the site was created as a result of a group or private channel in Teams, or not)
- Amount of GB used
- Primary administrators
- Template used
- Creation date
- Etc.
Also, on the "Active sites" page, administrators can create new sites with the "Create" command.
It is worth noting that accessing the SharePoint Admin Center to create a new site offers a unique advantage, which is the ability to use additional templates compared to the default ones available on the SharePoint home page. These are templates that administrators can use to avoid starting from scratch when creating a site, while also providing functionality not available in the templates accessible to regular users.
Active sites in the SharePoint Admin Center
Deleted sites, to see deleted SharePoint sites
(and decide what to do with them)
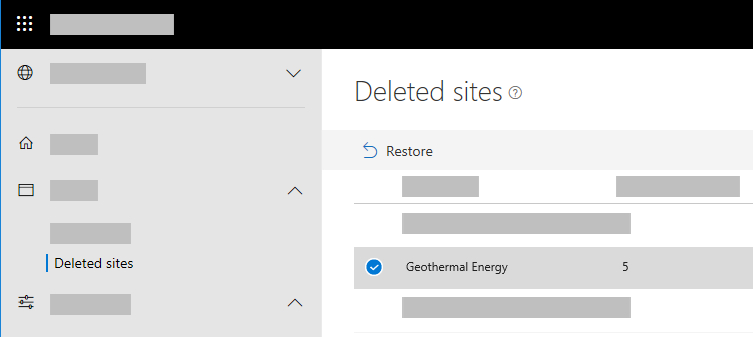
Just below the "Active sites" section, we find "Deleted sites", which allows you to access the page in the SharePoint Admin Center dedicated to deleted sites (but not permanently).
The feature to highlight on this page is the "Restore" command, which can be used to restore deleted SharePoint sites. This is very useful, especially when a site is deleted by mistake. But be careful: administrators have a limited time to restore a site, after which SharePoint sites in the "Deleted sites" area are permanently deleted.
The time available for restoration varies depending on the type of site.
Except for SharePoint sites linked to a Teams channel (which must be restored within 30 days of deletion directly from Microsoft Teams), team and communication sites can be restored in this area of the SharePoint Admin Center within 93 days of their deletion. Here's how:
- Select the sites to restore from the list presented in the "Deleted sites" area.
- Click on the "Restore" command in the top left corner.
Once 93 days have passed, the sites are completely removed from the SharePoint Online environment. To avoid losing important data, it is recommended to perform a backup or rely on third-party solutions to archive the information of a site that, although unused, may prove useful in the future.
"Restore" command in the deleted sites section of the SharePoint Admin Center
Policies for sharing and access to content in SharePoint
Under the "Policies" section, there are two very important areas in the SharePoint Admin Center.
These are the areas that gather the sharing and access configurations, respectively.
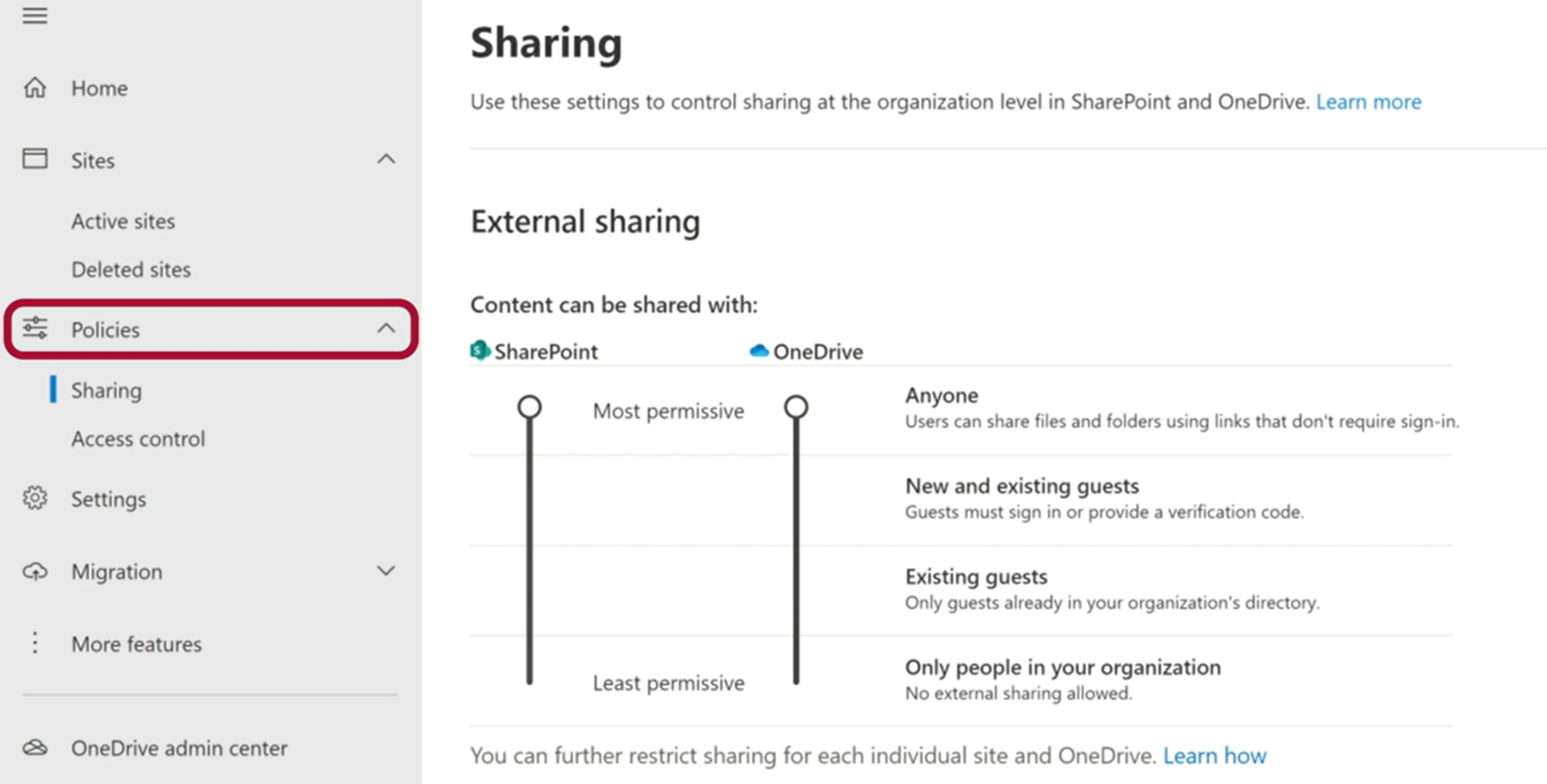
Starting with the "Sharing" area, administrators have the ability to define limits for sharing content in SharePoint and OneDrive. Specifically, four levels are available:
- Sharing with anyone
- Sharing with new and existing guests
- Sharing with existing guests only
- Sharing with people in the organization only
Administrators can then choose the level, from the most permissive for sharing links and files without sign-in, to the most restrictive for sharing with those who have a business account. The second area of interest under "Policies" is called "Access control" and offers more advanced settings compared to the "Sharing" area for protecting SharePoint and OneDrive files.
In "Access control", there are four categories of settings to manage access to content:
- Unmanaged Devices. Administrators can allow, limit, or block access for devices that do not belong to the business domain or that have operating systems or browsers that do not meet the configuration set for SharePoint.
- Inactivity Timeout. A security option used to set an inactivity period, after which a user is notified and eventually signed out.
- Network Location. The configuration that allows filtering access to SharePoint Online based on the user's IP address. For example, administrators may allow access only to users using the corporate network.
- Legacy Authentication. The setting to allow or block access from third-party applications or old Microsoft Office applications (Office 2010 and earlier) that cannot enforce device-based restrictions.
The "Sharing" and "Access control" areas together offer a wide range of options for deciding who can access what in the corporate SharePoint environment, adapting platform permissions to the organization's security policies in a flexible and granular way.
File sharing settings in the SharePoint Admin Center
Settings, to access further configurations
In the general "Settings" section of the SharePoint Admin Center, there are settings for:
- Choosing the way to manage notifications.
- Specifying the Home sites in your SharePoint instance.
- Defining default configurations for creating new sites.
- Managing limits for the storage space used by each site.
- Etc.
In practice, you can find here the settings to customize the corporate SharePoint environment.
As for a Home site, it is a site that serves as the landing page, providing a single access point to the SharePoint Online environment. Administrators can set a communication site (e.g., the company intranet) as the Home site to expand its search scope and centralize news and content useful to all users.
Term store, to modify the taxonomy of SharePoint sites
By selecting the "Term store" option in the SharePoint Admin Center, you are directed to the page where you can manage the metadata of your sites.
Metadata are the information underlying the search and content storage system in SharePoint Online sites. Therefore, the settings on the "Term store" page play a key role in the proper management of SharePoint and the business data it hosts.
Administrators can create or modify the local taxonomy for a SharePoint site here, working at the level of tags, term sets, and individual terms that can be customized with properties such as name, description, and usage designations.
It is possible to assign a person or group of users to a specific term set. In this case, the assigned labels do not grant additional permissions, but they help identify (or rather, track) users through a set of terms such as, for example, a job title and department.
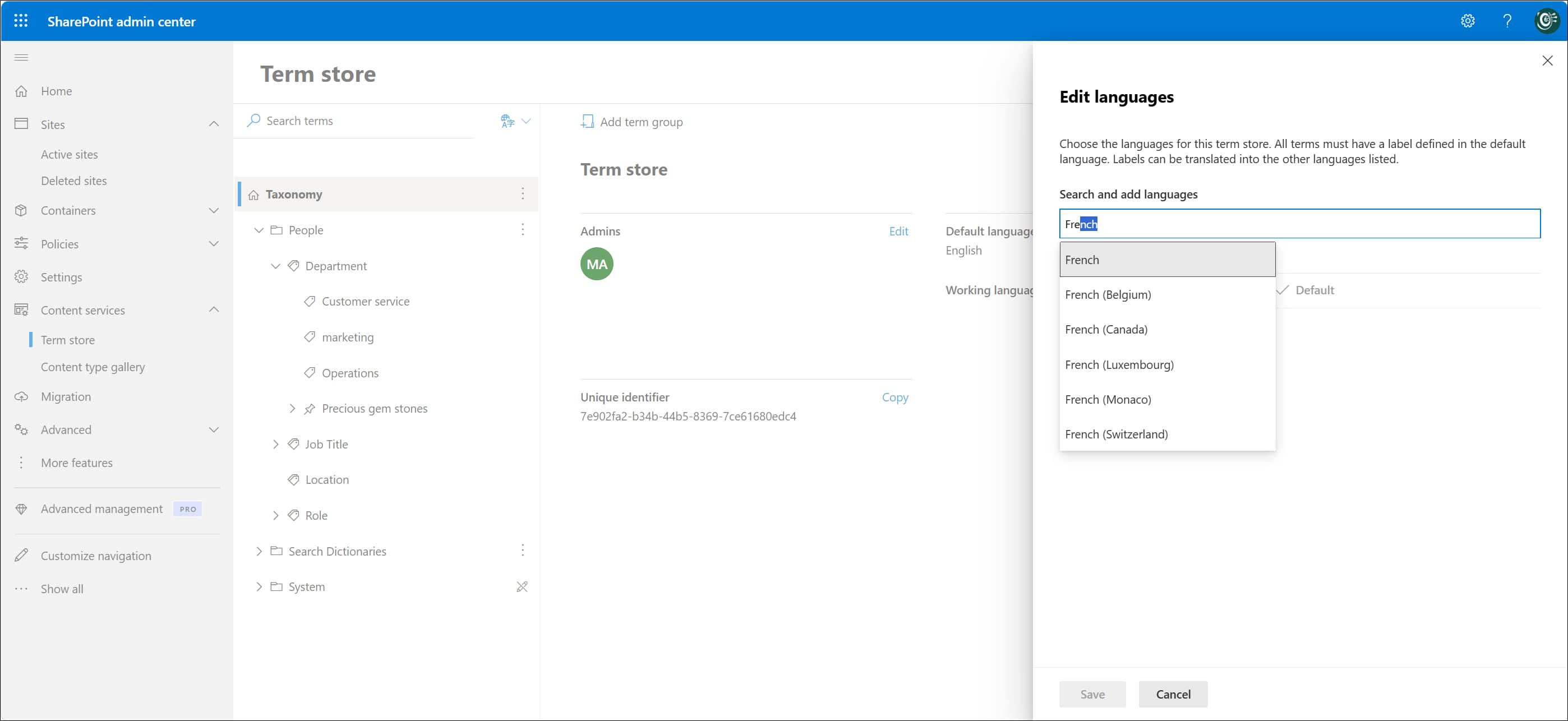
Defining the term store language in the SharePoint Admin Center
Migration, to manage migration processes in SharePoint
The SharePoint Admin Center provides a tool designed to manage migration processes: it is Migration Manager, which can be found under the "Migration" section in the left navigation bar.
Migration Manager brings together the settings for migrating to SharePoint Online, supporting the transfer of data from platforms such as Microsoft Stream, Dropbox, and Google Workspace.
Also in this area, the SharePoint Migration Tool is available for download. This tool is useful for migrating content from older versions of SharePoint On-Prem or from files taken from network folders.
SharePoint Admin Center: How to transfer data from Google to Microsoft with Migration Manager
Advanced, to access advanced configurations
In the "Advanced" section of the SharePoint Admin Center, administrators are offered some advanced configurations that are used, among other things, to manage the permissions required by custom applications that are installed in SharePoint Online.
These are settings that contribute to managing the extension capabilities of the platform, allowing intervention on the permissions that custom components have to interact with data in SharePoint or, more generally, in the corporate Microsoft 365 environment.
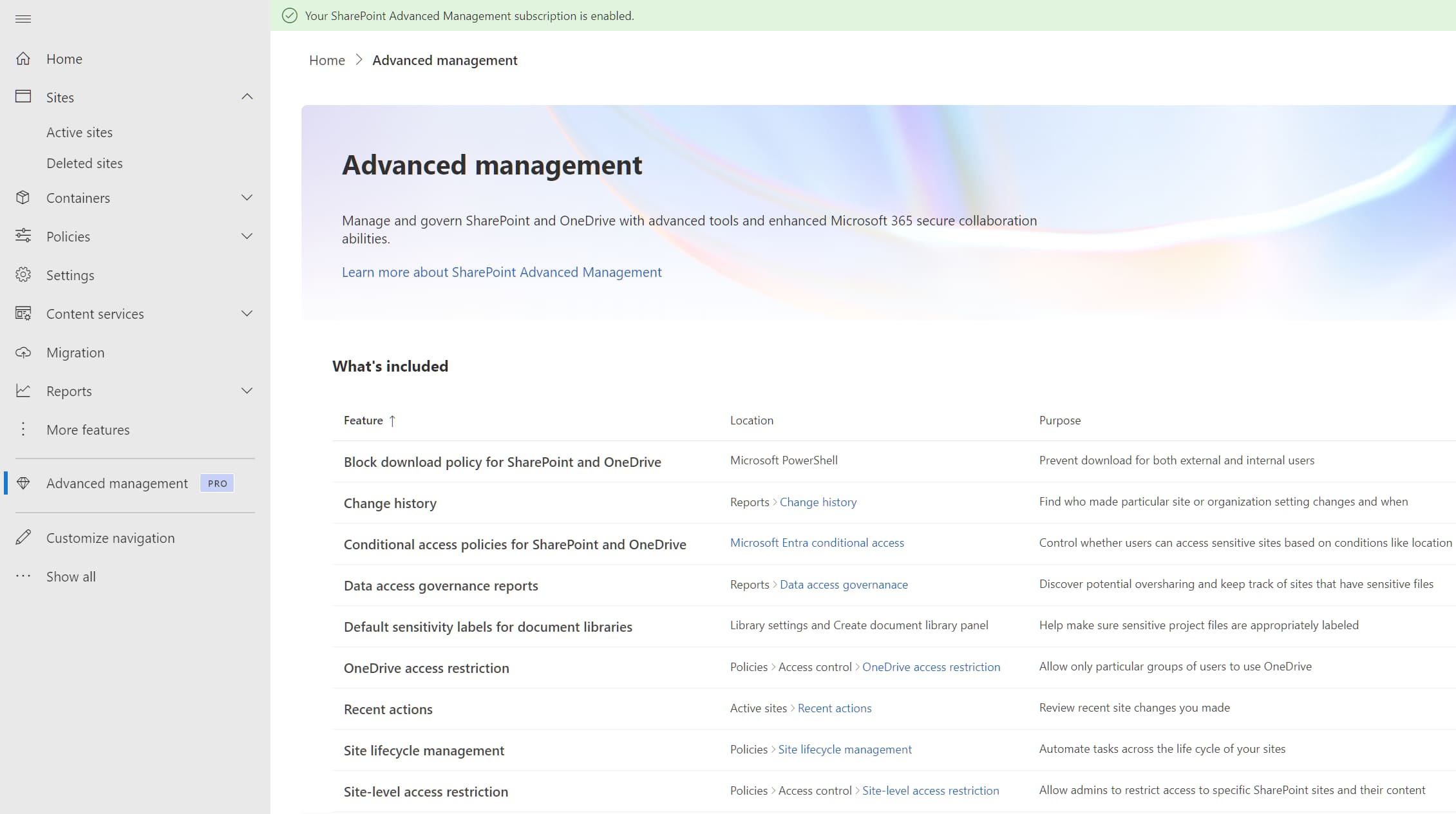
Overview of advanced management in the SharePoint Admin Center
To conclude this brief overview, below is a summary table of the main features and configurations available for SharePoint Online admins in the respective admin center.
| SharePoint Admin Center area | Available features |
| Home page |
|
| Active sites |
|
| Deleted sites |
|
| Policies |
|
| Settings |
|
| Term store |
|
| Migration |
|
| Advanced |
|
Need a hand managing your SharePoint sites?
We've got more than 100 on deck to support your company in:
- Distributing the right permissions to users
- Ensuring the security of shared information
- Improving document and resource management
- Developing custom web parts and branded graphics
Giuseppe Marchi
Microsoft MVP for SharePoint and Microsoft 365 since 2010.
Giuseppe is the founder of intranet.ai and one of the top experts in Italy for all things Microsoft 365. For years, he has been helping companies build their digital workspace on Microsoft's cloud, curating the people experience.
He organizes monthly online events to update customers on what's new in Microsoft 365 and help them get the most out of their digital workplace.

FAQ on the SharePoint Online Admin Center
What is the SharePoint Admin Center?
The SharePoint Admin Center is the web interface that provides SharePoint Online administrators with all the tools to manage sites, content, and data security in a centralized manner.
How do I access the SharePoint Admin Center?
Administrators must go to admin.microsoft.com, log in with their Office 365 credentials, and select the SharePoint admin center from the left-hand panel.
What are the main features of the SharePoint Admin Center?
The main features include creating new sites, managing access to content, monitoring storage usage, implementing collaboration and security policies, and managing the configurations of active SharePoint sites.
How do I assign the Admin role in SharePoint?
To assign the Admin role in SharePoint, global administrators must go to the Microsoft 365 admin center, select "Roles," then "Role Assignments," double-click on the "SharePoint Administrator" role, select "Add users," and add the users to whom the role will be assigned.
How do I restore a deleted SharePoint site?
To restore a deleted SharePoint site, administrators must go to the "Deleted sites" page in the SharePoint Admin Center, select the sites to restore, and click on the "Restore" command. This must be done within 93 days of deletion.
What are the sharing options in SharePoint?
Sharing options in SharePoint include sharing with anyone, with new and existing guests, with existing guests only, and with people in the organization only. These options can be configured in the "Sharing" section of the SharePoint Admin Center.
What is a Home site in SharePoint Online?
A Home site in SharePoint Online is a site that serves as a landing page, providing a single point of access to the SharePoint Online environment. Administrators can set up a communication site as a Home site to centralize news and content for all users in the organization.
Keep on reading
Microsoft 365 Archive: What It Is, Limits, and Alternatives

Microsoft 365 Archive extends storage in Microsoft 365, enabling the archiving of SharePoint sites. Let's see features, costs, and alternative solutions.
SharePoint Consulting: Why Choose intranet.ai?

Let's see who SharePoint Online consultants are and what they do, why it is beneficial to rely on their services and how to choose the right experts.
SharePoint Online vs SharePoint On-Prem: What's Better?

Here’s what to know about SharePoint On-Prem and SharePoint Online to make the best choice. Let’s explore their features, benefits, and differences.


